Total Keyhole Gastropexy
Laparoscopic Gastropexy
What is Laparoscopic Gastropexy?
Laparoscopic gastropexy is an innovative surgical procedure designed to securely attach the stomach to the abdominal wall, effectively preventing dangerous twisting, known as volvulus, in cases of GDV. This condition is a serious emergency that demands prompt action due to its potential for severe health issues. By utilising laparoscopic gastropexy, we can provide a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery, resulting in a range of advantages for your pet’s recovery and overall well-being.
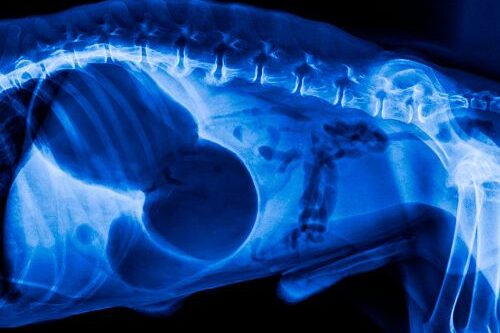
What is GDV (Gastric Dilatation -Volvulus)?
Indications for Laparoscopic Gastropexy:
Preventative Measure
In breeds predisposed to GDV, especially those with a deep chest, such as Great Danes, Doberman Pinschers, and Boxers.
Treatment for GDV
In cases where GDV has occurred, laparoscopic gastropexy may be performed concurrently with the treatment of the condition.
Benefits Laparoscopic Gastropexy?
Minimally Invasive
- Small Incisions: Laparoscopic gastropexy involves only a few small incisions rather than a large open incision. This reduces the amount of tissue disruption during the procedure.
- Reduced Trauma: Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, leading to a more gentle surgical experience for the patient.
Reduced Pain
- Reduced Discomfort: Because the incisions are smaller and less tissue is manipulated, there is generally less post-operative pain and discomfort.
- Effective Pain Management: Many patients experience lower levels of pain, which can often be managed with fewer pain medications.
Shorter Hospitalisation
- Same-Day Discharge: Many patients are able to go home the same day or the following day, reducing their time spent in the hospital.
- Reduced Risk of Hospital-Acquired Infections: Shorter hospital stays decrease the risk of infections and complications that can occur during longer hospitalisations.
Faster Recovery Time
- Quicker Healing: The minimally invasive nature of the procedure typically leads to faster healing of the incisions and surrounding tissues.
- Return to Normal Activities: Pets usually resume their normal activities more quickly compared to recovery from open surgery.
Lower Risk
- Reduced Infection Risk: Smaller incisions and less exposure of internal organs to the external environment lower the risk of postoperative infections.
- Fewer Surgical Complications: The precision of laparoscopic instruments reduces the likelihood of complications such as excessive bleeding or inadvertent damage to surrounding tissues.
Enhanced Precision
- Better Visualisation: The use of a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) provides high-definition images of the internal structures, allowing for greater precision in placing sutures and securing the stomach.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: The enhanced visualisation helps reduce the likelihood of accidental injury to surrounding organs and tissues.
Minimally Scarring
- Minimal Scarring: The small incisions used in laparoscopic surgery result in less noticeable scars compared to larger open surgical wounds.
- Better Aesthetic Outcome: Pet owners often appreciate the improved cosmetic appearance of the surgical site.
Reduced Complications
- Lower Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions and less tissue exposure reduce the overall risk of infection.
- Fewer Adhesions: The reduced trauma to tissues decreases the likelihood of developing internal adhesions (bands of scar tissue that can cause complications).
Reduced Surgical Time
- Efficient Procedure: Laparoscopic techniques can often be performed more quickly than traditional open surgeries due to the precision of the equipment and reduced need for extensive tissue manipulation.
- Lower Anesthesia Time: Shorter surgical times generally mean that the patient is under anesthesia for a shorter period, which can lower the associated risks.
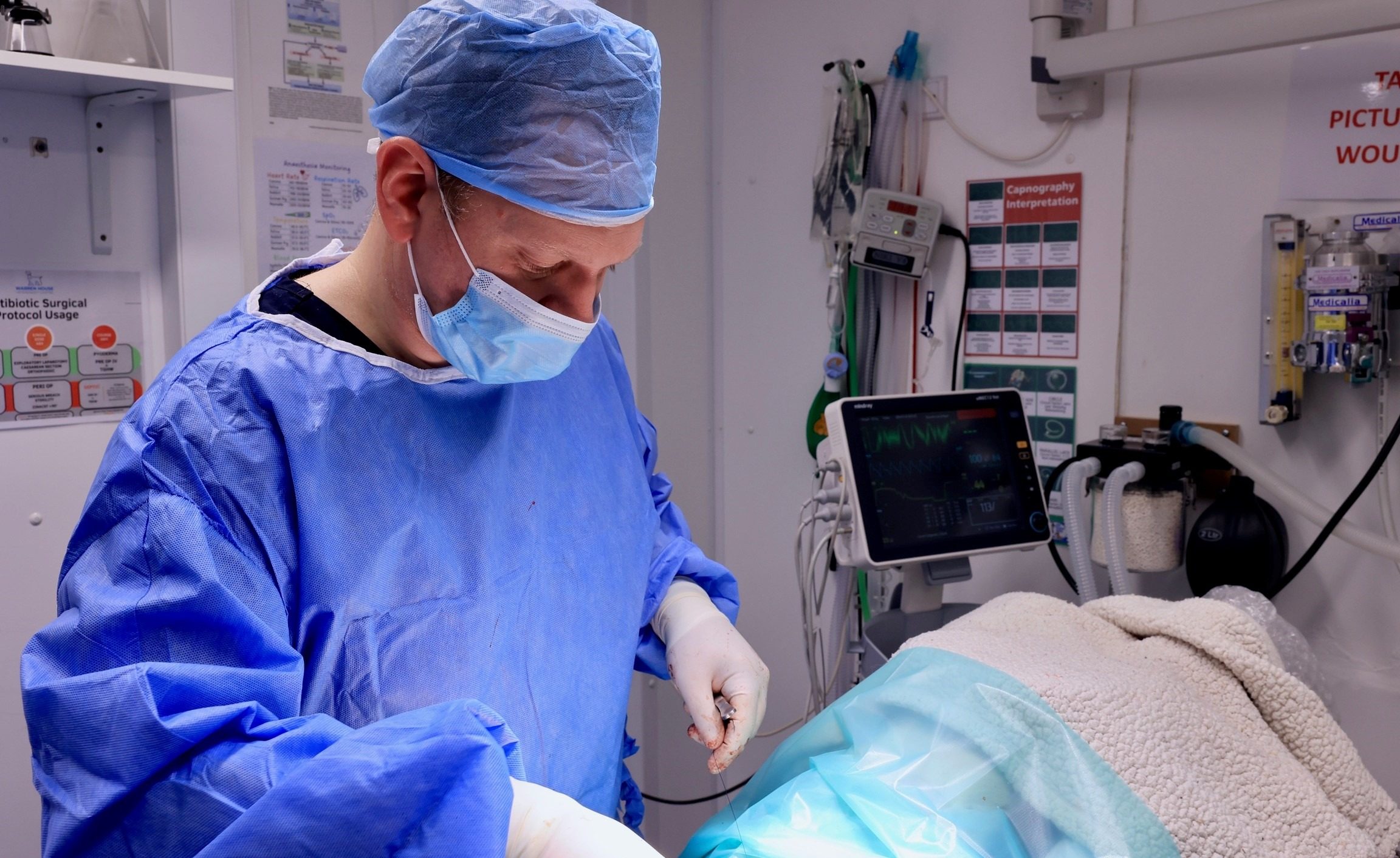
Laparoscopic Gastropexy Procedure: Step-by-step
Laparoscopic gastropexy can be performed simultaneously with a laparoscopic spay (ovariohysterectomy) in dogs, particularly in high-risk breeds prone to gastric dilatation-volvulus (GDV). Combining these procedures offers several benefits, including reduced overall anesthesia time and a single recovery period for the pet.

Preparation
- A comprehensive exam, including physical checks, blood tests, and imaging, ensures your pet is ready for surgery.
- General anaesthesia is adminstered

Surgery
- Incision and Trocar Placement: Small incisions are made in the abdomen, and trocars (hollow tubes) are inserted to allow access for the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
- Inflate the Abdomen: The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a working space for the procedure.
- Visualization: A laparoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera, is inserted to visualize the internal structures on a monitor.
- Gastropexy: The stomach is secured to the abdominal wall using sutures or staples. This prevents it from twisting in the future.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue, and the gas is released from the abdomen.

Post-Surgery Recovery
Your pet is monitored as they wake up from anaesthesia. Pain relief is provided as needed.
Aftercare & Recovery
FAQ
How does laparoscopic gastropexy differ from traditional gastropexy?
Laparoscopic gastropexy is less invasive than traditional gastropexy, using small incisions and a laparoscope for visualisation. In contrast, traditional gastropexy requires a larger incision and more tissue manipulation, resulting in longer recovery times and increased post-operative pain.
Are there any risks or complications associated with laparoscopic gastropexy?
- Infection: At the incision sites.
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding is possible but usually controlled during surgery.
- Anaesthesia risks: As with any procedure requiring anesthesia, there are inherent risks.
Schedule a consultation:
If your dog is at risk for GDV, a laparoscopic gastropexy can provide peace of mind by preventing this life-threatening condition. Contact us today to schedule a consultation or to learn more about this advanced preventive procedure.

