Retained Testicle
Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy
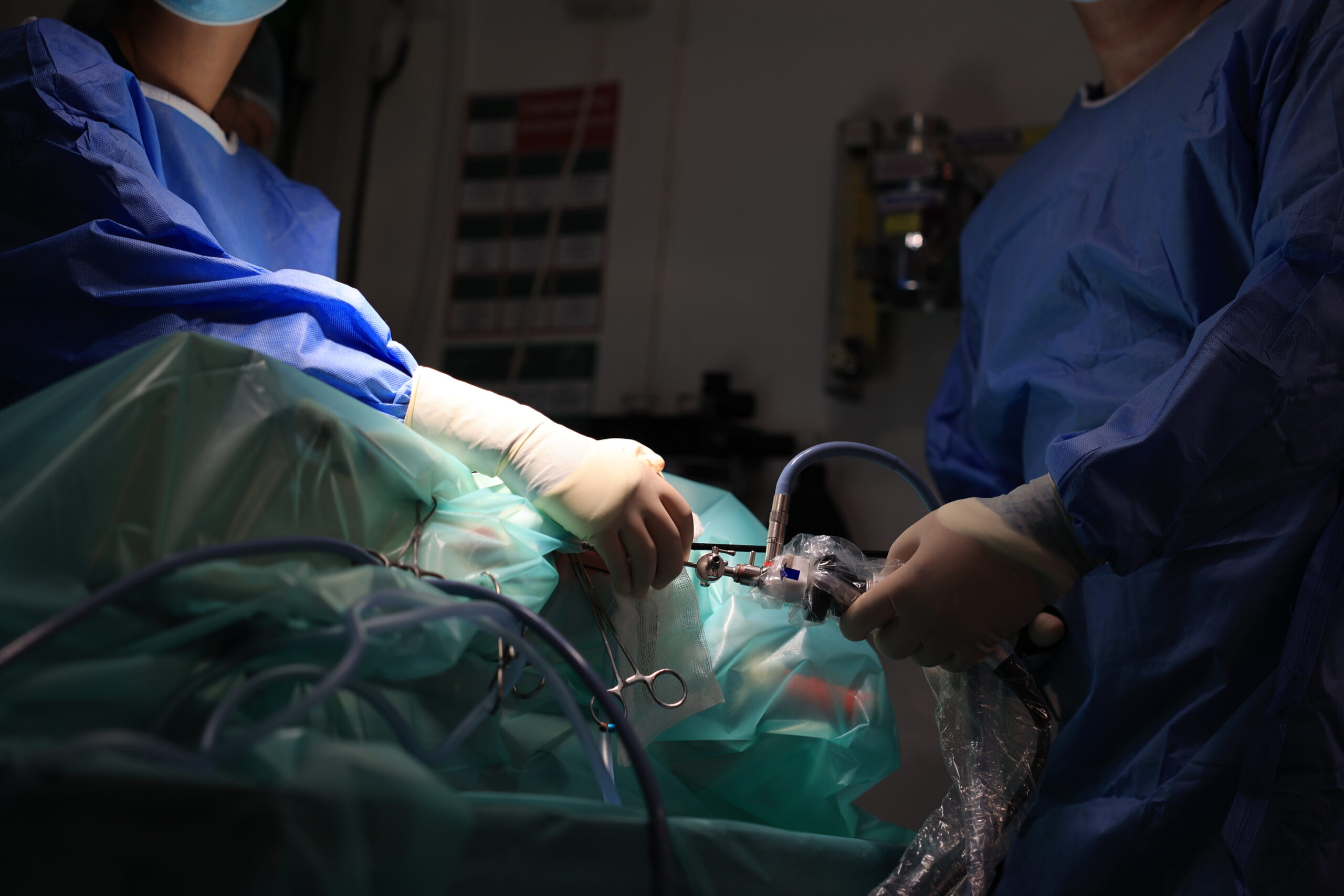
Introduction to Keyhole Cryptorchidectomy
Cryptorchidism is a prevalent congenital condition found in male animals, especially in dogs and cats, where one or both testicles do not descend into the scrotum. This condition can result in a range of health concerns, including a heightened risk of testicular cancer, torsion, and various behavioral problems. Timely diagnosis and intervention are essential to ensure the well-being of the affected animal, making it imperative for pet owners to monitor their furry companions closely.
What is Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy?
Laparoscopic cryptorchidectomy is an innovative and minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to effectively remove undescended testicles in animals. This advanced technique sets itself apart from traditional open surgery by utilising small incisions and a laparoscope, which is a slender tube fitted with a camera and specialised surgical instruments, ensuring a safer and more efficient experience for your pet.
Indications for Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy:
Unilateral or Bilateral Cryptorchidism
Whether one or both testicles are undescended, laparoscopic surgery is a viable option.
Abdominal or Inguinal Retained Testicles
The procedure is effective regardless of the location of the retained testicle.
Prevention of Complications
he surgery helps prevent serious complications associated with cryptorchidism, such as testicular cancer or torsion.
Benefits Laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy?
Minimally Invasive
- Smaller Incisions: Unlike traditional open surgery, laparoscopic cryptorchidectomy requires only a few small incisions. This minimises tissue damage and results in a more cosmetically appealing outcome.
- Reduced Tissue Trauma: The use of small incisions and specialised instruments reduces trauma to the surrounding tissues, promoting faster healing and less discomfort for the animal.
Reduced Pain
-
Reduced Pain Levels: The small incisions and minimal tissue disruption contribute to lower levels of postoperative pain, leading to a more comfortable recovery period for the animal.
Effective Pain Management: Pain is often managed more effectively with laparoscopic surgery, reducing the need for strong pain medications and the associated side effects.
Faster Recovery Time
- Quicker Postoperative Healing: Due to the minimally invasive nature of the procedure, pets often experience a quicker recovery. They typically resume normal activities sooner compared to traditional surgical methods.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Many animals undergoing laparoscopic cryptorchidectomy can go home the same day or after a very short hospital stay, minimising the stress of extended hospitalisation
Lower Risk
- Reduced Infection Risk: The small incisions used in laparoscopic surgery are less likely to become infected compared to larger open surgical wounds.
- Minimized Blood Loss: The precise nature of laparoscopic surgery often results in less bleeding, reducing the risk of significant blood loss during the procedure.
- Decreased Risk of Hernias: The smaller incisions and careful surgical techniques reduce the likelihood of postoperative hernias compared to traditional open surgery.
Enhanced Visualisation
- Enhanced Visualisation: The laparoscope provides a magnified view of the surgical area, allowing the veterinarian to see and work with greater precision. This enhanced visualisation helps ensure that the retained testicle is located and removed effectively.
- Precision in Removal: The laparoscopic tools allow for meticulous dissection and removal of the testicle, minimising the risk of damaging surrounding structures.
Minimally Scarring
- Minimal Scarring: The small size of the incisions results in minimal scarring, which is often less noticeable than the larger scars associated with traditional surgery.
- Faster Wound Healing: The smaller incisions heal more quickly, leading to a neater appearance and reduced post-surgical marks.
Reduced Complications
-
Easier Wound Care: Smaller incisions are easier to manage at home, requiring less frequent attention and reducing the chance of complications related to wound care.
-
Faster Return to Normal Activity: Pets can generally return to their usual routines more quickly, with less restriction on their activity levels compared to those recovering from traditional surgery.
Enhanced Safety
- Minimised Anaesthesia Time: The minimally invasive nature of the procedure often means a shorter anaesthesia time, which can be safer, especially for animals with underlying health conditions.
- Reduced Surgical Time: The efficiency of laparoscopic surgery often leads to a shorter overall surgical time, reducing the duration of anesthesia and associated risks.
Laparoscopic Spay Procedure: Step-by-step

Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Diagnosis: A thorough examination, including palpation and imaging (ultrasound or X-ray), to locate the retained testicle.
- Pre-Anesthetic Assessment: Blood tests and other diagnostics ensure the animal is fit for surgery.
- Fasting: The pet is typically fasted for 12 hours before the procedure.

Surgery
- Anesthesia: The animal is placed under general anesthesia to ensure it is pain-free and still during the surgery.
- Incision: Small incisions are made in the abdominal wall.
- Insertion of Laparoscope: The laparoscope and other surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions.
- Location and Removal of Testicle: The retained testicle is located using the camera and carefully excised.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue.

Post-Surgery Recovery
- Pain Management: Pain relief medications are administered post-surgery.
- Monitoring: The animal is monitored during recovery to ensure there are no complications.
Aftercare & Recovery
Limit your pet’s activity for a week to minimise stress on incision sites. Monitor the surgical area for signs of infection and ensure you follow your vet’s instructions for any prescribed medications like antibiotics or pain relief.
FAQ
How do I know if my pet has cryptorchidism?
Cryptorchidism is usually identified during routine veterinary exams. If one or both testicles are not palpable in the scrotum, further diagnostic tests may be recommended.
What are the risks associated with laparoscopic Cryptorchidectomy?
Laparoscopic cryptorchidectomy is generally safe but carries risks such as anaesthesia complications, infection, bleeding, and incomplete testicle removal. Postoperative issues might include pain, swelling, or residual tissue.

Schedule a consultation:
If you suspect your pet has cryptorchidism or want to learn more about laparoscopic cryptorchidectomy, please contact our clinic to schedule a consultation. Our team of experienced veterinarians is here to provide the highest standard of care for your beloved pet.

