
Knee Surgeries
Luxating Patella
A luxating patella, commonly known as a “floating kneecap,” occurs when the kneecap (patella) slips out of its normal position within the groove of the thigh bone (femur). This condition is particularly common in small dog breeds but can also affect cats and larger dogs. It can lead to intermittent lameness, discomfort, and, if left untreated, more severe joint issues.
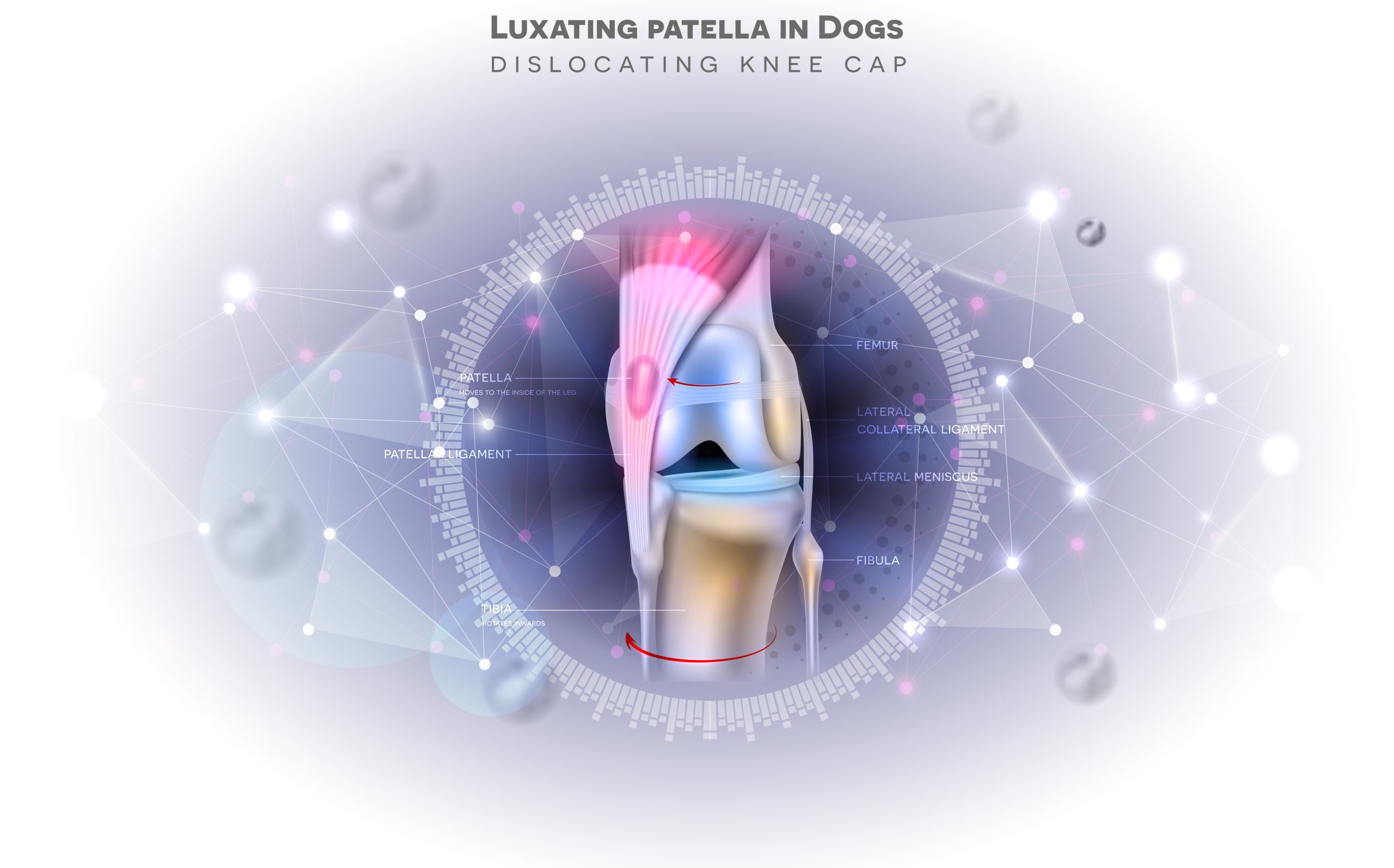
Causes of Luxating Patella?
- Genetics: It is often an inherited condition, particularly in small breeds like Pomeranians, Chihuahuas, and Yorkshire Terriers.
- Trauma: Injuries to the knee can lead to patellar luxation.
- Anatomical Abnormalities: Structural issues in the bones or muscles can predispose a pet to this condition
Risk Factors
- Breed: Small dog breeds are more commonly affected.
- Age: Young dogs may show signs early, but older pets can also develop the condition due to wear and tear.
- Weight: Obesity can exacerbate the problem by putting extra stress on the knee joint.
Signs and Symptoms
- Limping or Skipping: Pets may intermittently hold up the affected leg or skip while walking.
- Knee Popping: You might notice the knee joint “popping” in and out of place.
- Lameness: In severe cases, pets may struggle to walk or bear weight on the affected leg.
- Pain: Pets may show signs of discomfort, such as yelping or reluctance to move.
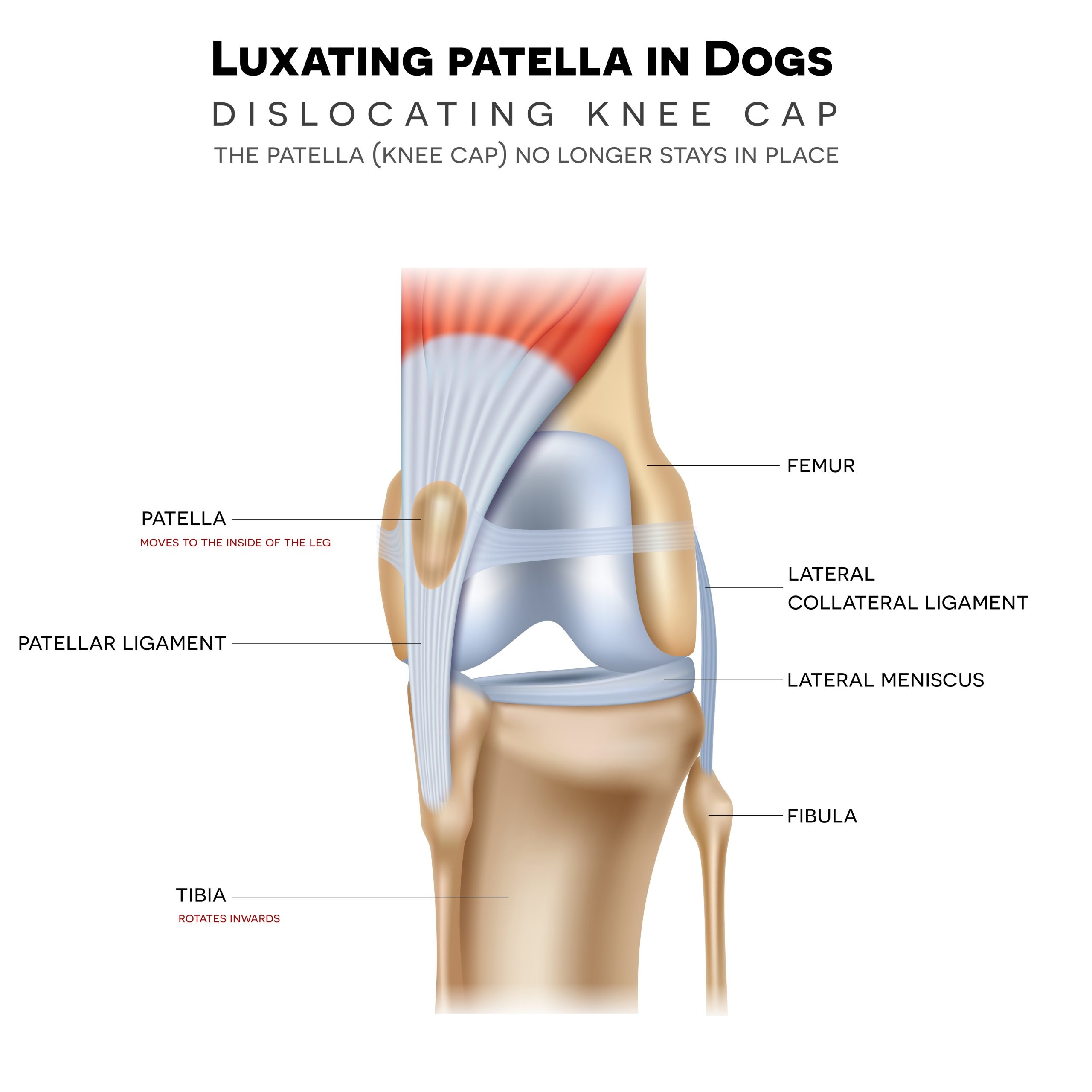
Diagnosing Patella Luxation
If you suspect your pet has a luxating patella, a veterinary examination is essential. Our veterinarian will:
- Physical Exam: Manipulate the knee to see if the patella can be luxated or if it’s already out of place.
- X-rays: Imaging may be used to assess the severity of the condition and check for any associated bone abnormalities.
Luxating Patella Grading

The patella luxates occasionally but returns to its normal position on its own.

The patella luxates more frequently and may need manual manipulation to return to position.

The patella is out of place most of the time but can be manually repositioned.

The patella is permanently out of place and cannot be repositioned manually.
Surgical Treatment Options
Soft Tissue Surgery
Trochleoplasty
Trochleoplasty is a surgical procedure designed to reshape the groove in the femur where the patella resides, creating a deeper and more stable channel that significantly reduces the risk of patellar luxation. During the procedure, the surgeon carefully modifies the trochlea to ensure it accommodates the patella more effectively, ultimately providing a more secure environment for the kneecap and minimising the likelihood of dislocation.
Tibial Tuberosity Transposition
FAQ
Can the Luxating Patella be managed?
Exercise modification involves limiting high-impact activities that could exacerbate the condition, while weight management focuses on maintaining your pet at a healthy weight to alleviate stress on the joints. Engaging in physical therapy with exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the knee can provide valuable stability to the patella. Additionally, pain management may be addressed through the prescription of medications such as anti-inflammatories to help mitigate discomfort.
Can Luxating Patella be prevented?
While you can’t always prevent a luxating patella, especially if it’s genetic, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Keeping your pet at an ideal weight reduces stress on the joints.
- Provide Proper Exercise: Regular, moderate exercise strengthens the muscles supporting the knee.
- Choose Breeders Wisely: If you’re selecting a pet from a breeder, ask about the history of luxating patella in the breeding lines.
Book A Consultation:
Restore your pet’s comfort and mobility! Schedule a consultation for luxating patella surgery today and help them live pain-free.

