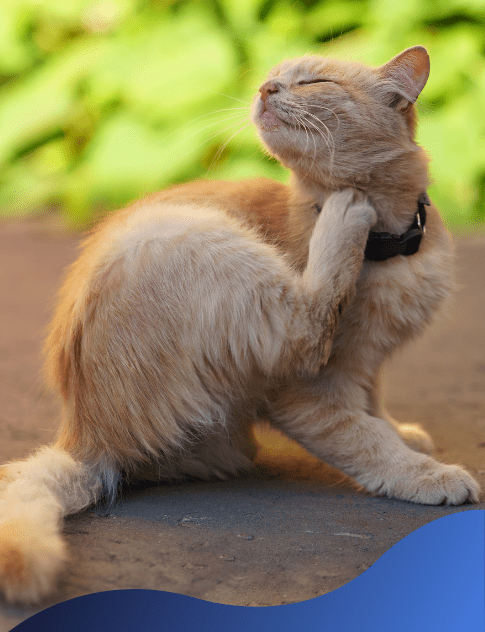
Most cats scratch every now and again, but excessive scratching indicates something is wrong. Itchy skin (Feline Pruritus) is a symptom of many different conditions.
Where fleas are not the answer, often a much more detailed and meticulous approach is needed to find the diagnosis.
Being the largest organ in the body, a cat’s skin acts as a protective barrier against the outside world. It helps them maintain the right body temperature and keep their hair and claws healthy. Developing a skin condition can make your cat feel unwell and treatment should not be delayed.
Itching-induced skin disease in cats can be challenging to differentiate from other skin diseases.
Signs Of Skin Conditions In Cats
Sometimes it’s easy to spot a skin problem in your cat, but other times it’s more difficult to understand. Different health conditions can cause similar skin reactions, and multiple skin problems can appear at the same time.
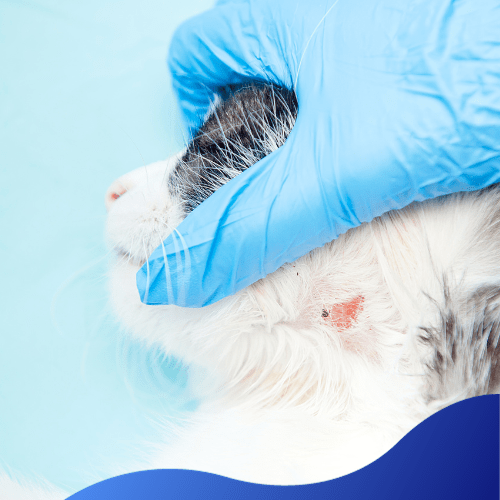
Common Skin Conditions In Cats
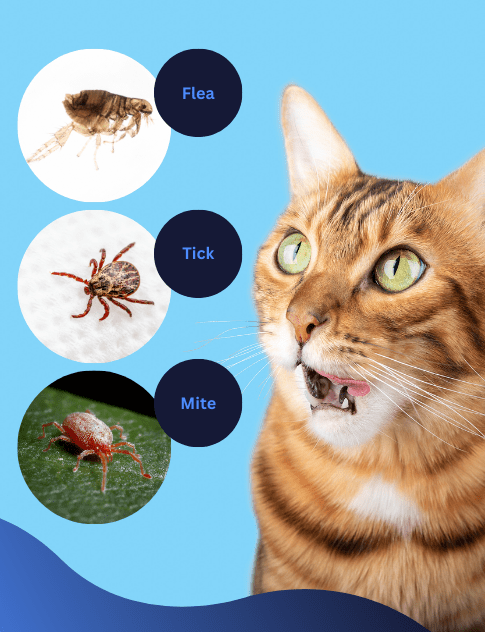
Parasites
- Fleas – little parasites that bite your cat and cause itching. Fleas can be a real problem, especially if your cat has a flea allergy. They can also be dangerous for young kittens where a heavy infestation can result in anaemia.
- Ticks – tiny blood-sucking parasites that look a bit like spiders. If you find a tick on your cat, it is important to remove it quickly and carefully using the appropriate equipment. As the tick attaches to your cat’s skin and grows, it can look like a sore on the skin.
- Mites – Microscopic parasites that are difficult to see with the naked eye. They are highly contagious and spread from cat to cat through direct contact or through infected bedding and grooming tools. Ticks are most commonly found in cats, causing intense irritation, itching, and redness.
Allergies
Flea bites are the most common cat allergy, causing skin reactions, discomfort, hair loss, fur chewing, or skin pain. The absence of fleas doesn’t necessarily rule out the allergy.
Cats, like humans, can develop allergies to everyday elements like pollen or dust mites, leading to contact dermatitis due to direct skin contact with allergens.
Cats may also experience intolerances or allergic reactions to certain food ingredients, even those they have previously eaten without issues.

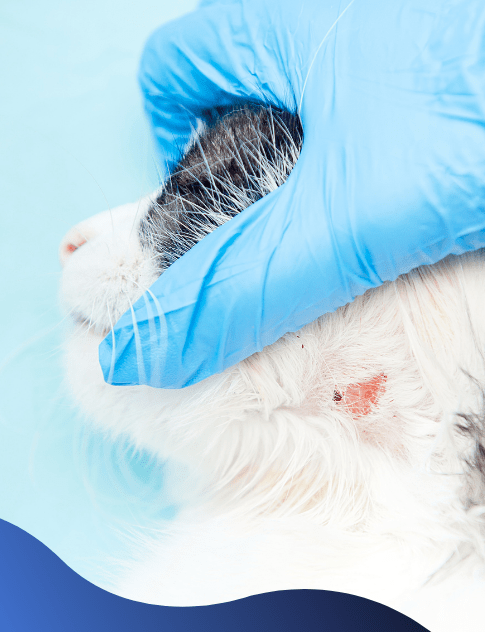
Infections
Cats often suffer from bacterial infections due to bites, wounds, or skin conditions like allergies, resulting in severe signs like scabs, ulcers, or redness on the skin.
Ringworm:
Ringworm is a contagious fungal infection affecting skin, hair, or nails, causing itching, hair loss, redness, crusting, and scaling. It’s most common in young or old cats, ill cats, and those with impaired immune systems, especially long-haired Persian cats.
Hair Loss
Cat hair loss, also known as alopecia, occurs when cats lose hair and develop bald patches.
Cats often remove hair by brushing or scratching, rather than falling out or not growing. They can be secretive and specific, sometimes forming a bald spot with a clear border.
This can be due to many different reasons, for example, skin diseases including allergies and ringworm can cause hair loss. Some cats experiencing stress or pain in a particular area may begin to over-groom and pull at their fur.
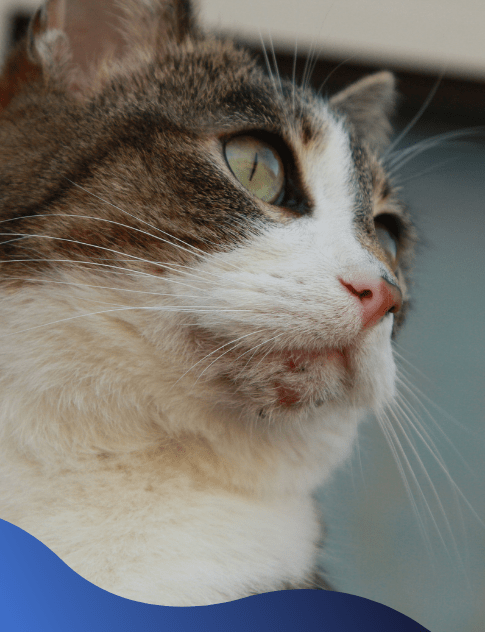

Feline Acne
Chin acne in cats is a condition where small dark specks or bumps remain around the cat’s mouth and chin. Causes include allergies, other health conditions, and secondary bacteria infections. To prevent this, switch to ceramic food bowls and clean them with any detergent.
Lumps and Bumps
Cats may develop lumps or bumps due to various causes, including insect bites, abscesses, cysts, and non-cancerous or cancerous tumors. Long-lasting growths, especially those spreading or changing color or shape, should be promptly examined by a vet.


Skin Ulcer
Skin ulcers are open sores on a cat’s body, often caused by injury, insect bites, or underlying medical conditions. They appear round, red, and inflamed, and require careful treatment. If your cat licks or scratches frequently, schedule an appointment with your veterinarian to investigate the underlying cause.
Skin Cancer
Cats can develop skin cancer due to abnormal cell growth, primarily caused by sun exposure. White and colored cats, lacking melanin pigment, are more susceptible to sun damage. Symptoms include hair loss, scabs, and unhealing sores. If left untreated, sunburn can progress to skin cancer, which can be treated with surgery. The most effective treatment for skin cancer in cats is surgery.

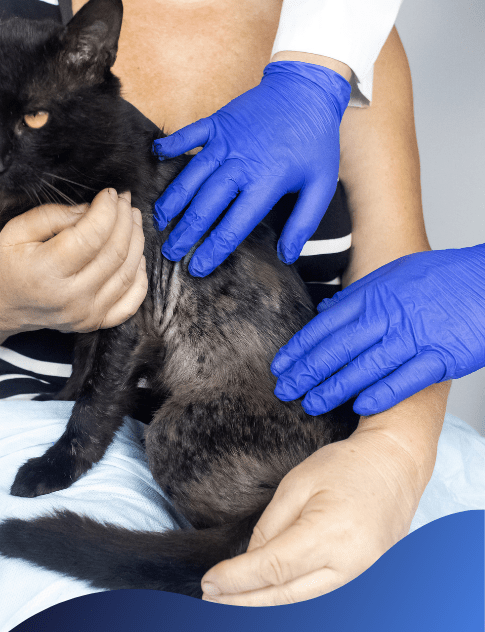
Diagnosing Cat Skin Problems
Vets are crucial for examining skin conditions in cats to ensure prompt treatment. They may ask about the cat’s history, lifestyle changes, and other signs. They may also conduct further tests to identify possible causes and examine the condition.
Click here to find out more about diagnosing skin problems.
Treating Skin Conditions In Cats
Your cat may need a combination of treatments to manage the underlying condition together with additional treatment to relieve any itchiness, discomfort or, secondary infections.
We may recommend cat skin treatments, such as:
- parasite control
- diet trials
- topical cream
- anti-inflammatory or antibiotic medications
Some skin conditions cannot be cured but may be controlled through lifelong treatment.
If you have any concerns regarding your dog’s skin condition, excessive scratching biting, and licking:
Thank you for reading, we hope you have found this article helpful, until next time…

