What is the difference?
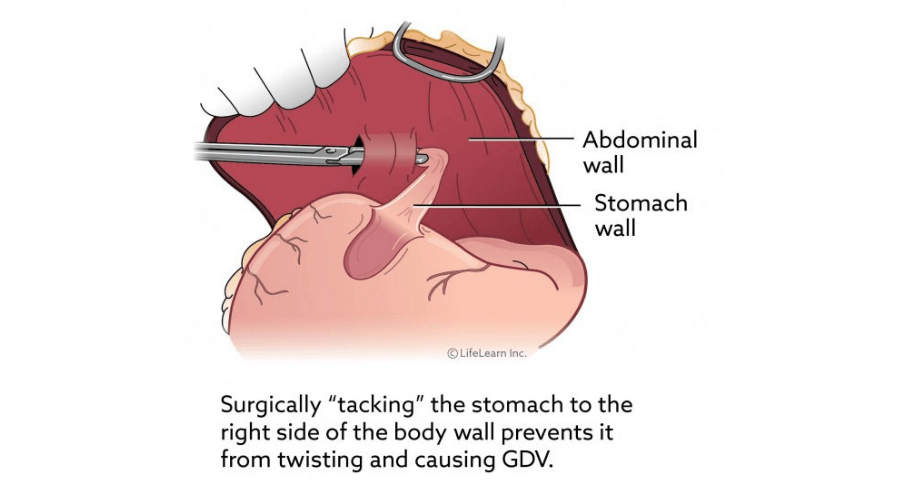
Gastropexy is a surgical procedure used to attach the stomach to the abdominal wall to prevent gastric dilatation-volvulus (GDV), commonly known as bloat. In pets, particularly dogs, several types of gastropexy are performed, each with its own specific techniques and purposes.
Here are the main types:
Incisional Gastropexy
Procedure: A small incision is made in the stomach wall and a corresponding incision in the abdominal wall. These incisions are then sutured together.
Advantages: Relatively simple and quick, with a lower complication rate.
Disadvantages: Not as secure as some other methods.
Belt Loop
Procedure: A strip of the stomach wall (a belt) is passed through a loop created in the abdominal wall and then sutured in place.
Advantages: Provides a secure attachment.
Disadvantages: More complex than incisional gastropexy.
Circumcostal Gastropexy
Procedure: A flap of the stomach wall is wrapped around a rib and sutured.
Advantages: Very secure attachment.
Disadvantages: Technically challenging and carries a higher risk of complications.
Tube Gastropexy
Procedure: A tube is placed between the stomach and the abdominal wall, and sutured in place, often used as a temporary measure.
Advantages: Useful for temporary decompression and feeding access.
Disadvantages: The tube must be removed later, and it is not intended as a permanent solution.
Laparoscopic-Assisted Gastropexy (LAG)
Procedure:
- Hybrid Approach: Combines laparoscopy and open surgery.
- Port Placement: One or two small incisions for the laparoscope and instruments.
- Visualisation: The laparoscope helps in visualising the stomach and abdominal wall.
- Exteriorisation: A small incision is made in the abdominal wall, and the stomach is partially pulled through this incision.
- Suturing: The stomach is sutured to the abdominal wall using traditional suturing techniques outside the body, then returned to the abdominal cavity.
Advantages:
- Combination of Techniques: Utilises the benefits of both laparoscopic and open surgery.
- Reduced Pain and Faster Recovery: Compared to fully open surgery, there is less postoperative pain and a quicker recovery.
- Simpler Suturing: Easier to perform the suturing compared to intracorporeal suturing in full laparoscopic surgery.
Disadvantages:
- Technical Expertise: Requires knowledge of both laparoscopic and open surgical techniques.
- Equipment Cost: Similar to LG, it requires laparoscopic equipment.
Laparoscopic Gastropexy (LG) (Recommended Method) ⭐
Procedure:
- Full Laparoscopy: Entirely performed using laparoscopic instruments without any need to exteriorize the stomach.
- Port Placement: Several small incisions (ports) are made for the insertion of the laparoscope and specialized instruments.
- Visualisation: The laparoscope provides a detailed, magnified view of the abdominal cavity.
- Suturing: The stomach is sutured to the abdominal wall using laparoscopic tools. Often, a specialised needle driver and suture material are used to perform an intracorporeal suturing technique
Advantages:
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions and less tissue disruption.
- Reduced Pain and Faster Recovery: Due to the minimally invasive nature.
- Improved Visualisation: The magnified view can help in precise suturing.
Disadvantages:
- Technical Complexity: Requires significant expertise in laparoscopic techniques.
- Equipment Cost: Requires specialised laparoscopic equipment
Our focus is on providing full Laparoscopic Gastropexy (LG) for pets, particularly those at risk for gastric dilatation-volvulus (GDV). We have the facilities, equipment, and expertise necessary to carry out this advanced procedure and prefer this method due to its numerous benefits.
We hope you have found this article useful, until next time…