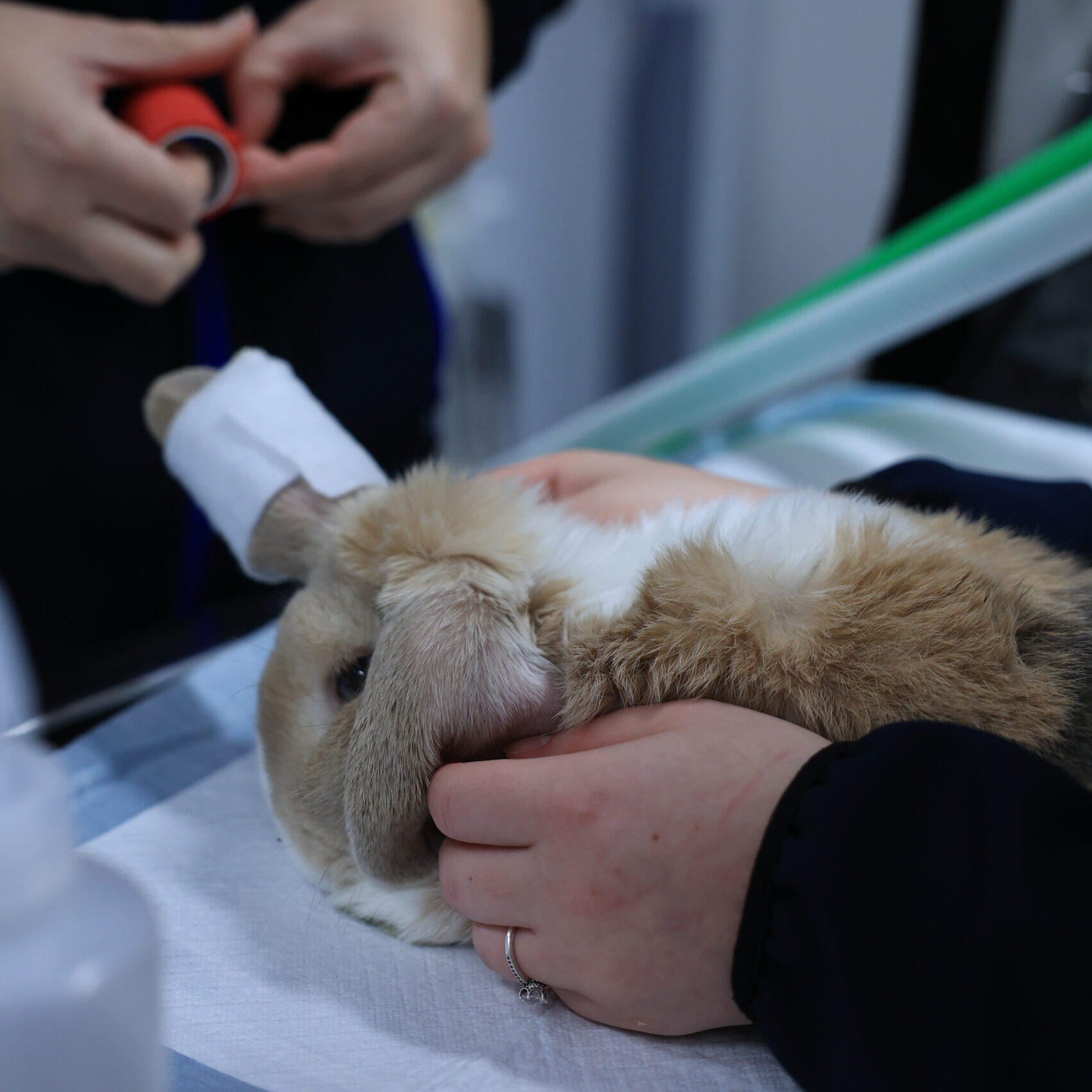
What Is Neutering?
Neutering in male rabbits is known as castration.
Neutering in female rabbits is known as spaying.
We recommend neutering all pet rabbits to prevent unwanted pregnancies and avoid health problems like ovarian and testicular cancer. Neutered rabbits also tend to be more sociable/less likely to fight with other bunnies.
Benefits Of Neutering Your Rabbit?
We recommend neutering all pet rabbits to prevent unwanted pregnancies and avoid health problems like ovarian and testicular cancer. Neutered rabbits also tend to be more sociable/less likely to fight with other bunnies.
NO RISK OF PREGNANCY
Pregnancy is a tough time and rabbits don’t get the emotional rewards we can get from reproducing.
Rabbits can give birth to several litters per year, and pregnancy and birth can be risky for your rabbit and kittens. (Yes baby rabbits are called kittens)
IMPROVES SOCIALISATION
Rabbits need a companion, and one person is not enough, imagine not having friends who speak your language!
Guinea pigs are also not suitable companions.
Neutering of both is really important, as male and female pairings are usually better socially.
LOWER RISK OF CANCER
Unfortunately, female rabbits are very susceptible to uterine (womb) cancer relatively early in life.
They may also have uterine infections or other cancers such as breast (breast tissue) cancer.
Spaying at a young age greatly reduces the chances of this happening.
IMPROVED BEHAVIOUR
Unneutered rabbits can be aggressive, temperamental and difficult to handle, which is really important to be mindful of if you have children.
REMOVE THE RISK OF FALSE PREGNANCIES
Unneutered female rabbits often develop false pregnancies, which can cause hormonal behaviour such as aggression towards their owners and other rabbits.
NO URINE SPAYING
Unneutered rabbits are less likely to spray urine to mark their territory.
When Should I Neuter My Rabbit?
Rabbits are usually neutered when they are 4 to 5 months old.
Males can be neutered as early as 10-12 weeks, although we may want to wait a little longer, especially with smaller rabbits.
Care should be taken with male rabbits after castration- they can still be fertile for up to four weeks because semen can still be in the genital tract!
Be sure to separate them from the unneutered females for at least a month after surgery.
What Is The Difference In Procedures?
CASTRATION
If your rabbit is male, our vet will make a small incision over each testicle so that they can be carefully removed. Performed as a minor surgical operation under general anaesthetic.
SPAYING
If your rabbit is female, your vet will make a small incision along the middle of her abdomen (tummy) so her ovaries and uterus (womb) can be carefully removed. Performed as a routine surgical operation under general anaesthesia.
Book A Consultation To Discuss
Post Operative Care & Recovery
There are several things you can do to speed up the recovery process.
REST
After the surgery, your rabbit may be a bit sleepy and disorientated from the anaesthesia, this can last a couple of hours.
Make sure your rabbit is kept bonded with their partner and provide them with a calm place to rest.
Give them some of their favourite greens, as well as their normal hay and pellets.
WATCH & MONITOR
It is important to watch and monitor your rabbit to make sure they are eating normally, are pain-free and well in themselves.
Check the incision site at least twice a day to make sure it is clean and none of the stitches has become loose or nibbled.
Keep their living space very clean to prevent the wound from infection.
Should you have any worries or concerns, always contact the practice.
Not Registered? Join us, it will only take a minute
Don’t worry, we are still registering new clients and would love to have you and your beautiful cats on board.
REGISTER